In comparison to typical students students who are exceptional – In the realm of education, the comparison of exceptional students to typical students has ignited profound interest. This essay delves into the multifaceted differences between these two groups, examining their academic performance, cognitive abilities, social and emotional development, educational needs, identification and assessment, and effective instructional strategies.
As we embark on this exploration, we uncover the unique strengths and challenges faced by exceptional students, highlighting the importance of tailored educational approaches to foster their academic success and overall well-being.
Academic Performance
Exceptional students often exhibit significant differences in academic performance compared to typical students. They may excel in certain areas while facing challenges in others. Research has shown that exceptional students typically have higher IQ scores and perform better on standardized tests.
They may also have advanced reading comprehension and vocabulary skills.
However, exceptional students may also struggle with executive functioning skills, such as organization, time management, and attention. They may also have difficulty with social interactions and emotional regulation, which can impact their academic performance.
Factors Contributing to Differences, In comparison to typical students students who are exceptional
- Cognitive abilities
- Learning styles
- Motivation and engagement
- Environmental factors
- Access to resources and support
Cognitive Abilities

Exceptional students often possess unique cognitive abilities that distinguish them from typical students. They may have advanced problem-solving skills, strong memory, and exceptional creativity.
Specific areas where exceptional students excel include:
- Spatial reasoning
- Logical thinking
- Verbal fluency
- Processing speed
Implications for Educational Practices
Understanding the cognitive abilities of exceptional students is crucial for developing effective educational practices. Teachers can tailor instruction to meet their unique learning needs, providing them with challenges that foster their cognitive growth.
Social and Emotional Development

Exceptional students may experience social and emotional development differently compared to typical students. They may have difficulty with social interactions, such as understanding social cues and forming friendships.
Exceptional students may also experience challenges with emotional regulation. They may be more sensitive to sensory stimuli and have difficulty managing their emotions.
Challenges and Opportunities
- Social isolation
- Bullying
- Anxiety and depression
- Development of self-advocacy skills
- Opportunities for peer support
Recommendations for Support
- Social skills training
- Emotional regulation strategies
- Peer mentoring programs
- Parent and teacher support
Educational Needs

The educational needs of exceptional students differ significantly from those of typical students. They require individualized support and accommodations to reach their full potential.
| Educational Need | Exceptional Students | Typical Students |
|---|---|---|
| Academic support | Differentiated instruction, specialized tutoring, assistive technology | Standard curriculum, minimal support |
| Social-emotional support | Social skills training, counseling, peer support | Limited support or focus |
| Specialized services | Occupational therapy, speech therapy, physical therapy | Rarely required |
Implications for Educational Planning
Educational planning for exceptional students must consider their unique needs. Schools must provide a range of supports and services to ensure their academic, social, and emotional well-being.
Identification and Assessment
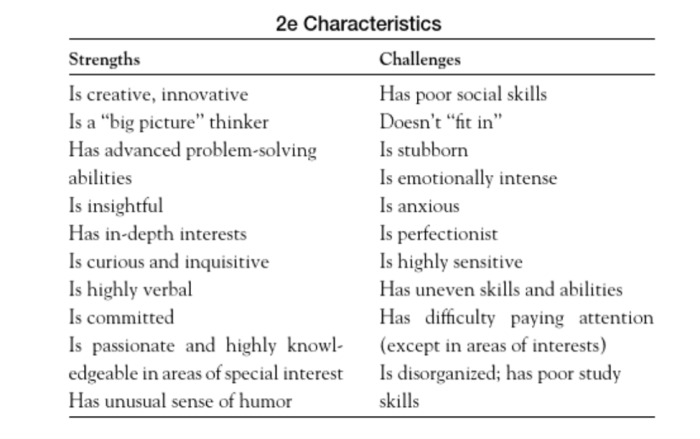
Accurate and timely identification and assessment are crucial for providing appropriate support to exceptional students.
- Observation:Teachers and parents can observe students’ behavior and performance to identify potential areas of concern.
- Screening:Standardized tests or brief assessments can screen for potential learning disabilities or other exceptionalities.
- Formal assessment:Comprehensive evaluations by psychologists or other professionals provide detailed information about a student’s cognitive, academic, and social-emotional functioning.
Challenges and Limitations
- Bias in assessment tools
- Cultural and linguistic diversity
- Time and resource constraints
al Strategies: In Comparison To Typical Students Students Who Are Exceptional
Effective al strategies can significantly enhance the learning experience for exceptional students.
| al Strategy | Exceptional Students | Typical Students |
|---|---|---|
| Differentiation | Tailored instruction, flexible grouping, varied materials | Minimal differentiation |
| Accommodations | Extended time, assistive technology, preferential seating | Rarely required |
| Assistive technology | Speech-to-text software, text-to-speech software, sensory aids | Not typically required |
Research Support
Research has consistently shown that the use of effective al strategies can improve academic outcomes, social-emotional development, and overall well-being for exceptional students.
Q&A
What are the key differences in academic performance between exceptional and typical students?
Exceptional students often demonstrate advanced academic abilities, excelling in areas such as mathematics, reading, and science. They may exhibit exceptional problem-solving skills, critical thinking, and a deep understanding of complex concepts.
How do the cognitive abilities of exceptional students compare to those of typical students?
Exceptional students typically possess strong cognitive abilities, including enhanced working memory, processing speed, and attention. They may also exhibit exceptional reasoning, abstract thinking, and problem-solving skills.
What are the unique social and emotional challenges faced by exceptional students?
Exceptional students may face challenges in social and emotional development, including difficulty with social cues, communication, and peer relationships. They may also experience anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues at higher rates than typical students.



