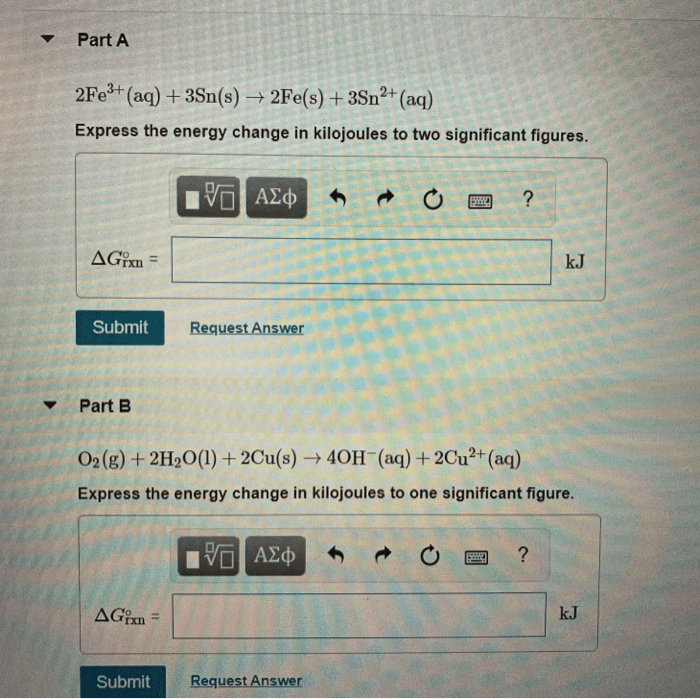
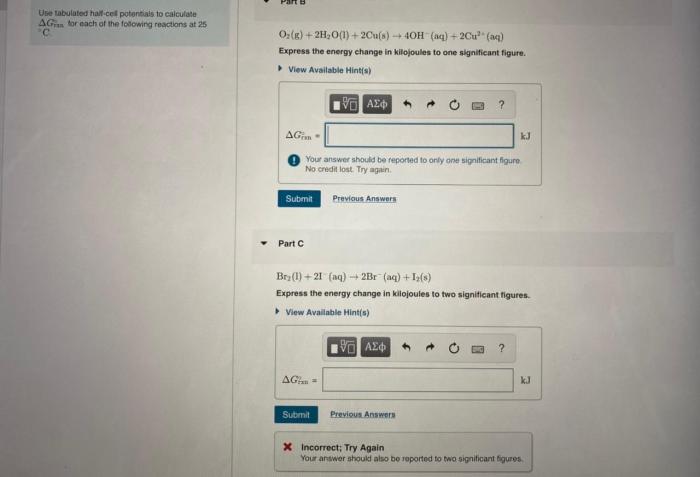
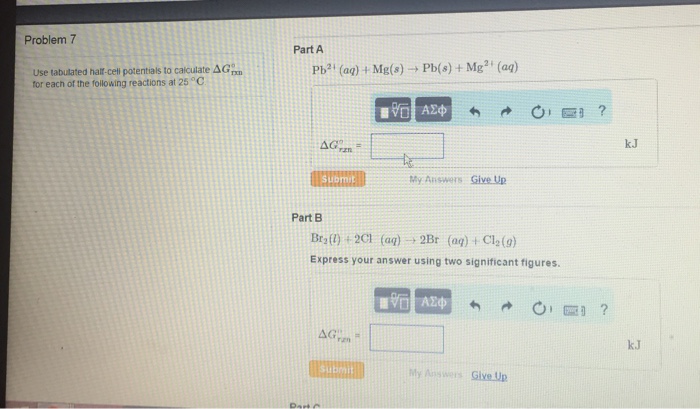
Use the tabulated half cell potentials to calculate – Calculating standard cell potential using tabulated half cell potentials is a crucial aspect of electrochemistry. This method provides a comprehensive understanding of electrochemical reactions and their applications. By leveraging tabulated half cell potentials, we can determine the potential difference between two half-cells and predict the spontaneity and direction of redox reactions.
This technique involves identifying half-reactions, understanding their significance, and utilizing tabulated half-cell potentials to calculate the standard cell potential. The applications of standard cell potential extend to battery design, electroplating, and other electrochemical processes. However, it is essential to consider the limitations of this approach to ensure accurate predictions in real-world scenarios.
Calculating Standard Cell Potential: Use The Tabulated Half Cell Potentials To Calculate
Standard cell potential, denoted by E o, is a measure of the electromotive force of an electrochemical cell under standard conditions. It is a crucial parameter that determines the spontaneity and efficiency of electrochemical reactions.
Standard cell potential can be calculated using the formula: E o= E ocathode– E oanode, where E ocathodeand E oanodeare the standard reduction potentials of the cathode and anode half-reactions, respectively.
Identifying Half-Reactions
Half-reactions are the individual oxidation and reduction reactions that occur in an electrochemical cell. They can be identified by using tabulated half-cell potentials, which list the standard reduction potentials of various half-reactions.
To identify the half-reactions, first determine the overall reaction occurring in the cell. Then, split the reaction into two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction. The half-reaction with a more positive standard reduction potential is the reduction half-reaction, while the other is the oxidation half-reaction.
Tabulating Half-Cell Potentials, Use the tabulated half cell potentials to calculate
Tabulated half-cell potentials provide a convenient reference for identifying half-reactions and calculating standard cell potentials. These tables list the standard reduction potentials of various half-reactions, organized by the type of electrode material and the electrolyte solution used.
For example, a typical table of half-cell potentials might include:
- Hydrogen electrode (SHE): 0.00 V
- Silver/silver ion electrode: +0.80 V
- Copper/copper ion electrode: +0.34 V
- Zinc/zinc ion electrode: -0.76 V
Applications of Standard Cell Potential
Standard cell potential has numerous practical applications, including:
- Battery design:Standard cell potential is used to determine the voltage output and capacity of batteries.
- Electroplating:Standard cell potential is used to control the deposition of metal ions onto a substrate during electroplating.
Limitations of Standard Cell Potential
While standard cell potential is a valuable tool for understanding electrochemical reactions, it has certain limitations:
- Non-standard conditions:Standard cell potential assumes standard conditions (298 K, 1 atm pressure, 1 M concentration). Deviations from these conditions can affect the actual cell potential.
- Irreversible reactions:Standard cell potential is not applicable to irreversible reactions, where the reverse reaction does not occur spontaneously.
- Complex reactions:Standard cell potential does not account for complex reactions involving multiple steps or intermediates.
Questions and Answers
What is the significance of using tabulated half cell potentials?
Tabulated half cell potentials provide a standardized reference for comparing the reducing and oxidizing strengths of different half-reactions. They allow for the prediction of the spontaneity and direction of redox reactions.
How can I identify half-reactions from tabulated half-cell potentials?
Half-reactions can be identified by examining the tabulated half-cell potentials. The half-reaction with a more positive potential is the reduction half-reaction, while the half-reaction with a more negative potential is the oxidation half-reaction.
What are the limitations of using standard cell potential for real-world applications?
Standard cell potential calculations assume ideal conditions, which may not always be present in real-world applications. Factors such as temperature, concentration, and the presence of impurities can affect the accuracy of the calculated potential.