Cannulation of thoracic duct cpt code – Cannulation of the thoracic duct, a procedure involving the insertion of a catheter into the thoracic duct, plays a crucial role in various medical interventions. This article delves into the specific CPT code associated with this procedure, exploring its components, modifiers, and the intricate steps involved in its execution.
Furthermore, we examine potential complications and post-procedure care considerations, providing a comprehensive overview of cannulation of the thoracic duct.
Introduction
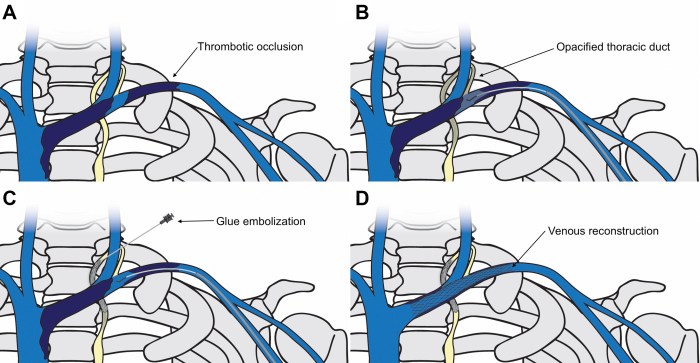
Cannulation of the thoracic duct is a surgical procedure that involves inserting a catheter into the thoracic duct, a lymphatic vessel that drains lymph from the upper body and empties it into the bloodstream.
This procedure is primarily used for the collection of chyle, a milky fluid that contains lymphocytes, fats, and proteins. Chyle is essential for maintaining fluid balance and immune function in the body.
Purpose and Indications
Cannulation of the thoracic duct is typically performed for the following purposes:
- Collection of chyle:Chyle can be collected for various research purposes, such as studying the composition of lymph and immune function.
- Nutritional support:In patients with impaired gastrointestinal function, chyle can be used as a source of nutrition through enteral or parenteral administration.
- Treatment of chylothorax:Chylothorax is a condition in which chyle accumulates in the pleural space. Cannulation of the thoracic duct can be used to drain the chyle and relieve the symptoms.
CPT Code for Cannulation of Thoracic Duct
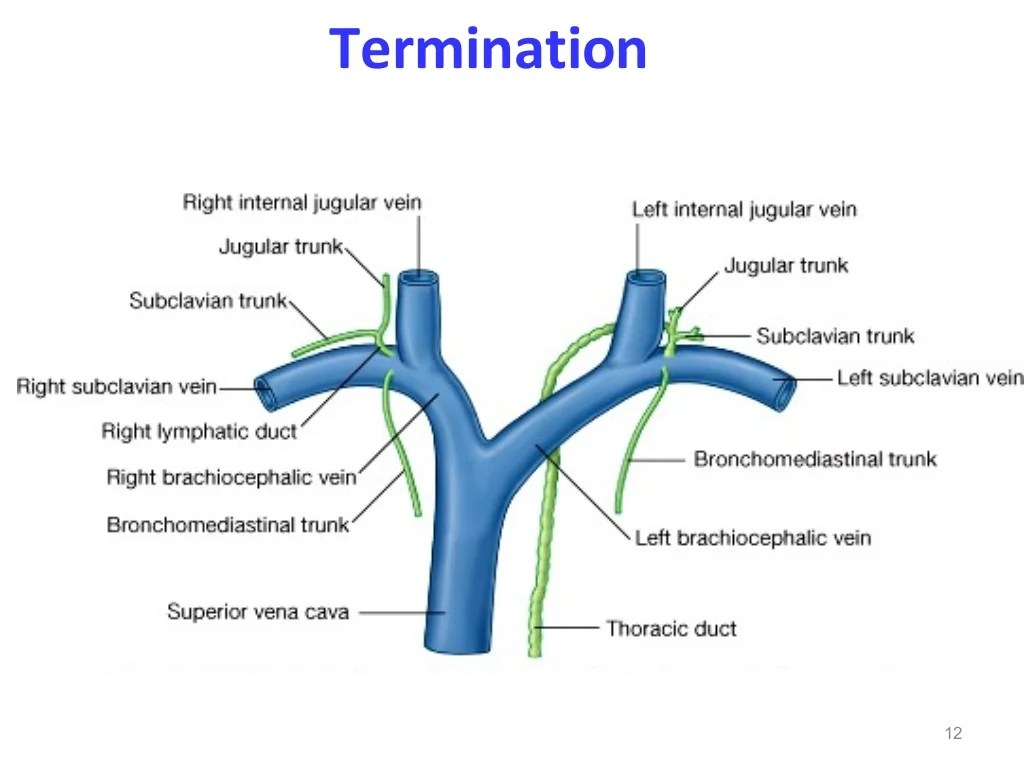
Cannulation of the thoracic duct involves inserting a catheter into the thoracic duct, a lymphatic vessel that drains fluid from the body’s tissues. This procedure is typically performed to collect lymphatic fluid for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes.
Specific CPT Code
The specific CPT code for cannulation of the thoracic duct is 38790.
Components and Modifiers of the CPT Code
- 38790: Cannulation of thoracic duct; open
The following modifiers may be used with CPT code 38790:
- -50: Bilateral procedure
- -59: Distinct procedural service
- -76: Repeat procedure by the same physician
Procedure for Cannulation of Thoracic Duct
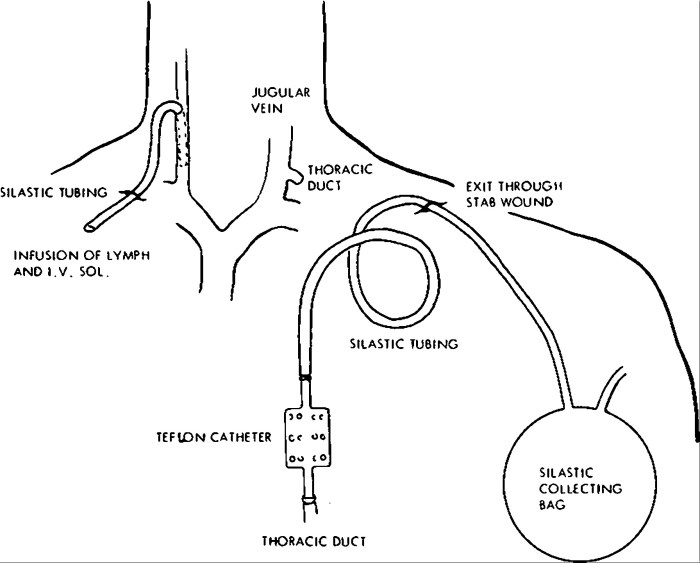
Cannulation of the thoracic duct involves inserting a cannula into the thoracic duct to collect chyle, a milky fluid that contains fats and other nutrients absorbed from the small intestine. The procedure is typically performed in a hospital setting under general anesthesia.
Patient Positioning
The patient is positioned supine with the head and neck extended. The arms are abducted and placed on arm boards.
Anesthesia
General anesthesia is typically used for cannulation of the thoracic duct. This ensures that the patient is comfortable and does not experience any pain during the procedure.
Surgical Technique
- A small incision is made in the skin over the thoracic duct.
- The thoracic duct is identified and dissected free from surrounding tissue.
- A cannula is inserted into the thoracic duct and secured in place.
- The incision is closed with sutures.
The cannula is typically left in place for several days to collect chyle. The chyle is then analyzed to assess the patient’s nutritional status and to monitor the absorption of nutrients from the small intestine.
Complications of Cannulation of Thoracic Duct
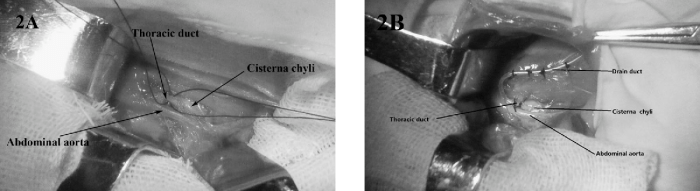
Cannulation of the thoracic duct is a procedure that carries the potential for complications. Understanding and managing these complications is crucial for the safety and well-being of the patient.
Complications can arise from the insertion of the cannula, the presence of the cannula in the duct, or the removal of the cannula. The most common complications include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Pneumothorax
- Chylothorax
- Lymphedema
Bleeding can occur during the insertion of the cannula, especially if the duct is inadvertently punctured. Infection can develop if the cannula is not properly sterilized or if the insertion site becomes contaminated. Pneumothorax is a condition in which air enters the pleural space, causing the lung to collapse.
This can occur if the cannula punctures the pleura, the lining of the lung. Chylothorax is a condition in which lymphatic fluid accumulates in the pleural space. This can occur if the cannula blocks the flow of lymphatic fluid from the thoracic duct.
Lymphedema is a condition in which lymphatic fluid accumulates in the tissues, causing swelling. This can occur if the cannula damages the lymphatic vessels or if the flow of lymphatic fluid is obstructed.
Prevention and Management
To prevent and manage complications, it is important to:
- Use aseptic technique during the insertion and removal of the cannula.
- Monitor the patient closely for signs of bleeding, infection, pneumothorax, chylothorax, or lymphedema.
- Treat any complications promptly.
By following these guidelines, the risk of complications from cannulation of the thoracic duct can be minimized.
Post-Procedure Care
Following the cannulation of the thoracic duct, meticulous post-procedure care is essential to ensure patient comfort, prevent complications, and promote optimal recovery.
Post-operative management involves vigilant monitoring, meticulous wound care, and effective pain management.
Monitoring
- Closely monitor vital signs, including blood pressure, heart rate, and respiratory rate.
- Assess for signs of infection, such as fever, chills, or drainage from the wound site.
- Monitor fluid balance and electrolyte levels to prevent dehydration or electrolyte imbalances.
- Regularly check the catheter site for any signs of bleeding, leakage, or infection.
Wound Care
Proper wound care is crucial to prevent infection and promote healing.
- Keep the wound site clean and dry.
- Change dressings regularly as directed by the healthcare provider.
- Avoid submerging the wound in water until it has fully healed.
- Inspect the wound for any signs of infection, such as redness, swelling, or discharge.
Pain Management
Adequate pain management is essential for patient comfort and well-being.
- Administer pain medication as prescribed by the healthcare provider.
- Use ice packs or cold compresses to reduce swelling and pain.
- Encourage rest and avoid strenuous activities that may aggravate pain.
Alternative Techniques: Cannulation Of Thoracic Duct Cpt Code
While the standard approach to thoracic duct cannulation remains the most widely used, alternative techniques have emerged to address specific patient needs or anatomical variations.
These alternative techniques offer varying advantages and disadvantages compared to the standard approach, and their selection depends on the individual patient’s condition and the surgeon’s expertise.
Fluoroscopic-Guided Cannulation
- Involves the use of fluoroscopy to guide the cannula insertion, providing real-time visualization of the thoracic duct’s anatomy.
- Offers increased accuracy and reduces the risk of complications, especially in patients with complex anatomy or variations in the thoracic duct’s location.
- Requires specialized equipment and expertise, and may be more time-consuming than the standard approach.
Ultrasound-Guided Cannulation, Cannulation of thoracic duct cpt code
- Utilizes ultrasound imaging to visualize the thoracic duct and guide the cannula insertion.
- Provides real-time visualization of the duct’s location and size, allowing for precise cannulation.
- Less invasive than fluoroscopic-guided cannulation, but requires specialized ultrasound equipment and operator skill.
Endoscopic Cannulation
- Involves the use of an endoscope to visualize the thoracic duct and insert the cannula.
- Allows for direct visualization of the duct and surrounding structures, reducing the risk of injury to adjacent tissues.
- Requires specialized endoscopic equipment and expertise, and may be more technically challenging than other techniques.
Laparoscopic Cannulation
- Employs laparoscopic techniques to access the thoracic duct through small incisions in the abdomen.
- Minimally invasive, reducing surgical trauma and recovery time.
- Requires specialized laparoscopic equipment and expertise, and may be more challenging in patients with adhesions or complex anatomy.
FAQs
What is the purpose of cannulating the thoracic duct?
Cannulation of the thoracic duct allows for the collection of lymphocytes, which are essential components of the immune system. These lymphocytes can be used for research purposes or for therapeutic applications such as adoptive immunotherapy.
What are the potential complications of thoracic duct cannulation?
Potential complications include bleeding, infection, and damage to the thoracic duct or surrounding structures. These complications can be minimized with proper technique and meticulous attention to detail during the procedure.