Expanse traveled by marco polo – Marco Polo’s travels stand as a testament to the boundless human spirit of exploration and discovery. His remarkable journey, spanning continents and cultures, forever altered our understanding of the world and left an enduring legacy that continues to inspire.
From the bustling streets of Venice to the exotic courts of the East, Marco Polo’s travels were a symphony of adventure and cultural exchange. He traversed treacherous lands, witnessed extraordinary civilizations, and returned with tales that ignited the imaginations of Europeans for centuries to come.
Marco Polo’s Travels and Explorations
Marco Polo’s travels in the 13th century were groundbreaking in the history of exploration and global knowledge. His detailed accounts of the East, which he documented in his book “The Travels of Marco Polo,” provided Europeans with their first glimpse into the vast and exotic cultures of Asia.
Marco Polo’s journey played a significant role in shaping the European worldview and inspiring future explorers.
Marco Polo’s Journey Timeline
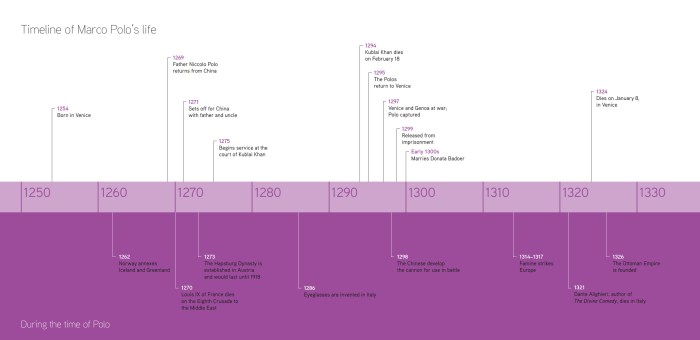
Marco Polo’s journey spanned over 24 years, from 1271 to He traveled extensively through Asia, visiting countries such as China, Persia, India, and Japan. Here is a detailed timeline of his journey:
- 1271:Marco Polo and his family set out from Venice on a trading expedition to the East.
- 1275:They reached the court of Kublai Khan in Beijing, where they spent 17 years.
- 1292:Marco Polo left China with a Mongol princess who was to marry the Persian ruler.
- 1295:Marco Polo returned to Venice, where he dictated his travelogue to a writer.
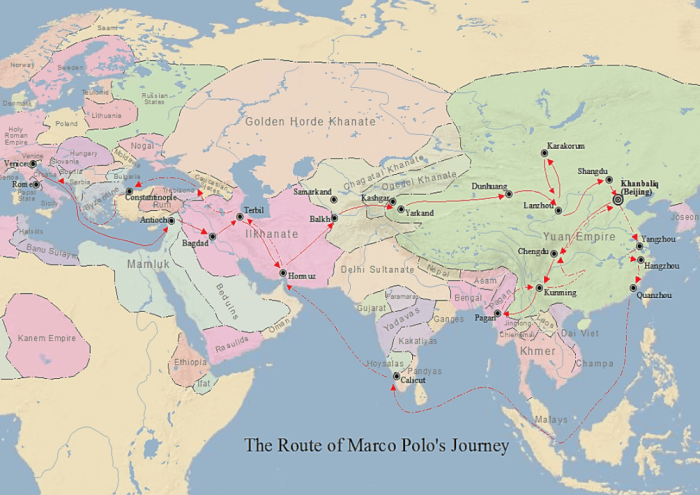
Routes and Destinations
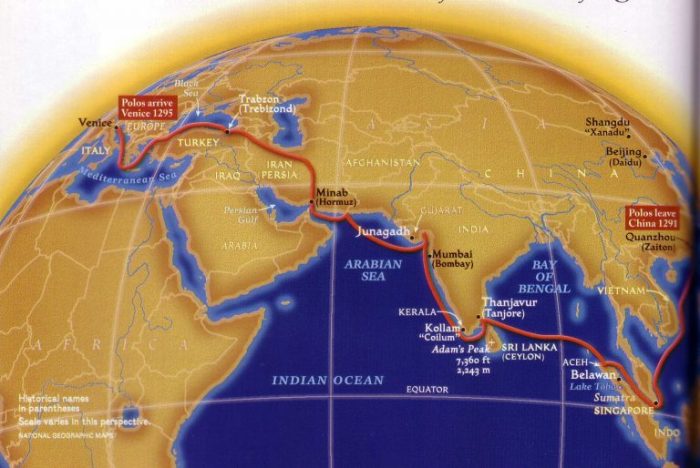
Marco Polo’s extraordinary journey spanned vast distances, covering numerous countries and regions. His extensive travels can be categorized into several distinct routes, each leading to remarkable destinations. The table below provides a comprehensive overview of the major routes and destinations encountered by Marco Polo, along with approximate distances traveled.
Routes and Destinations Traveled by Marco Polo
| Route | Destination | Distance Traveled |
|---|---|---|
| Central Asia Route | Xi’an (China), Karakorum (Mongolia) | Approximately 8,000 kilometers |
| Southern China Route | Quanzhou (China), Guangzhou (China) | Approximately 1,500 kilometers |
| Indian Ocean Route | Hormuz (Persia), Calicut (India) | Approximately 5,000 kilometers |
| Middle East Route | Baghdad (Iraq), Jerusalem (Palestine) | Approximately 3,000 kilometers |
| Mediterranean Sea Route | Constantinople (Turkey), Venice (Italy) | Approximately 4,000 kilometers |
Geographical Discoveries and Observations
Marco Polo’s extensive travels provided him with firsthand knowledge of vast regions and civilizations. His observations and descriptions played a crucial role in expanding the understanding of the world’s geography and cartography.
New Lands and Civilizations
Polo’s accounts introduced Europeans to numerous previously unknown lands and civilizations, including:
- China: Polo’s detailed descriptions of the Mongol-ruled Yuan Dynasty, including its capital, Dadu (modern Beijing), provided valuable insights into a civilization that was largely unknown in Europe.
- Japan: Polo’s mention of a land called “Zipangu” (Japan) sparked European interest in the East and fueled later expeditions, such as Christopher Columbus’s voyage.
- Southeast Asia: Polo’s accounts of the Malay Archipelago, Sumatra, and Java introduced Europeans to the rich and diverse cultures of Southeast Asia.
Corrections to Existing Maps
Polo’s observations also helped to correct existing maps and expand the known world.
- Shape of Asia: Polo’s descriptions of the vastness of Asia and the shape of its coastline challenged the prevailing belief that Asia was a rectangular landmass.
- Indian Ocean: Polo’s accounts provided accurate information about the size and shape of the Indian Ocean, correcting the exaggerated depictions found on earlier maps.
- African Coastline: Polo’s descriptions of the African coastline, including the Cape of Good Hope, contributed to the growing knowledge of Africa’s geography.
Impact on Cartography
Polo’s observations had a profound impact on cartography. His descriptions and sketches influenced the work of mapmakers such as Fra Mauro and Gerardus Mercator, who created more accurate and detailed maps of the world.
Cultural Encounters and Exchanges: Expanse Traveled By Marco Polo
Marco Polo’s travels brought him into contact with a wide range of cultures, from the cosmopolitan cities of the Middle East to the remote villages of China. These encounters provided him with a unique opportunity to observe and record the customs, beliefs, and technologies of these different societies.
One of the most striking aspects of Marco Polo’s travels was his encounter with the Mongol Empire. The Mongols were a nomadic people who had recently conquered a vast territory stretching from Eastern Europe to China. Marco Polo was fascinated by their military prowess and their unique way of life.
He spent several years in the Mongol court, where he learned about their language, customs, and religion.
Marco Polo’s travels also took him to China, where he spent over 15 years. During this time, he witnessed the extraordinary wealth and sophistication of the Chinese civilization. He marveled at the size and beauty of Chinese cities, the advanced technology of their shipbuilding, and the exquisite craftsmanship of their artisans.
Marco Polo’s travels had a profound impact on both the East and the West. He introduced Europeans to the wonders of the East, including the use of paper money, printing, and gunpowder. He also helped to spread knowledge of Chinese culture and technology throughout Europe.
Exchange of Ideas
Marco Polo’s travels facilitated the exchange of ideas between different cultures. He brought back to Europe knowledge of Chinese astronomy, mathematics, and medicine. He also introduced Europeans to the concept of paper money and printing.
In return, Marco Polo introduced Chinese scholars to European ideas about astronomy, geography, and medicine. He also helped to spread knowledge of Christianity in China.
Exchange of Technologies
Marco Polo’s travels also led to the exchange of technologies between different cultures. He introduced Europeans to the use of gunpowder, which revolutionized warfare. He also brought back to Europe knowledge of Chinese shipbuilding techniques, which led to the development of more advanced ships.
Marco Polo’s extensive travels exposed him to a tapestry of cultures and beliefs, each with its unique interpretations of symbols. One such symbol, the crow, has long carried allegorical meanings across various societies. Explore the allegorical meaning of a crow to gain insights into its associations with wisdom, prophecy, and even the supernatural.
As Marco Polo ventured through diverse lands, his encounters with these symbols deepened his understanding of the human experience and the interconnectedness of cultures.
In return, Marco Polo introduced Chinese scholars to European technologies such as the astrolabe and the compass. He also helped to spread knowledge of European mining and metalworking techniques in China.
Exchange of Goods
Marco Polo’s travels also facilitated the exchange of goods between different cultures. He brought back to Europe a wide range of Chinese goods, including silk, porcelain, and spices. He also introduced Europeans to the concept of paper money and printing.
In return, Marco Polo introduced Chinese scholars to European goods such as wool, glass, and metalwork. He also helped to spread knowledge of European mining and metalworking techniques in China.
Economic and Trade Impacts

Marco Polo’s extensive travels and detailed accounts played a pivotal role in shaping the economic and trade landscapes of the medieval world. His observations and reports provided a vital bridge between the East and the West, facilitating the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, thereby leaving an enduring impact on global trade networks.
Role in Facilitating Trade
Marco Polo’s travels provided invaluable insights into the vast trading networks of Asia, introducing European merchants to new and exotic products such as silk, spices, and precious stones. His writings sparked interest and demand for these goods in Europe, leading to increased trade volumes and the establishment of new trade routes.
Polo’s descriptions of the wealth and prosperity of the East, particularly China, encouraged European merchants to explore and establish trade connections with the region. His accounts helped to dispel misconceptions and fears about the unknown, making it more feasible for merchants to venture into unfamiliar territories.
Impact on Global Trade Networks
Marco Polo’s travels significantly altered the global trade landscape. The introduction of new products and trade routes stimulated economic growth and innovation in both the East and the West. The increased demand for Eastern goods led to the expansion of existing trade networks and the emergence of new ones, connecting Europe, Asia, and Africa.
Moreover, Polo’s observations and descriptions of the political and economic systems of the regions he visited contributed to a broader understanding of global affairs. His writings provided valuable information for merchants and policymakers alike, helping them to navigate the complexities of international trade.
Legacy and Influence
Marco Polo’s travels and writings had a profound and lasting impact on the world. His accounts of the East introduced Europeans to new cultures, customs, and technologies, and helped to shape the way Europeans viewed the world.
Dissemination of Knowledge about the East, Expanse traveled by marco polo
Marco Polo’s book, “The Travels of Marco Polo,” was one of the most widely read books in Europe during the Middle Ages. It provided Europeans with their first detailed account of the East, including descriptions of the Mongol Empire, China, India, and Southeast Asia.
Polo’s writings helped to dispel many of the myths and misconceptions that Europeans had about the East, and they played a major role in stimulating European exploration and trade.
Impact on Subsequent Exploration
Marco Polo’s travels also had a direct impact on subsequent exploration. His descriptions of the East inspired many Europeans to undertake their own journeys, including Christopher Columbus, who was motivated by Polo’s account of the riches of the East. Polo’s writings also helped to shape the routes that European explorers took, as they sought to follow in his footsteps.
Cultural Encounters and Exchanges
Marco Polo’s travels also led to a number of cultural encounters and exchanges between East and West. Polo introduced Europeans to new technologies, such as paper money and gunpowder, and he also brought back with him a number of Chinese artifacts, including porcelain and silk.
In turn, Polo’s writings introduced the East to European culture, and they helped to lay the foundation for future cultural exchanges between the two regions.
Economic and Trade Impacts
Marco Polo’s travels also had a significant impact on the economy and trade. His descriptions of the East helped to stimulate European demand for Eastern goods, and he also played a role in establishing trade routes between Europe and the East.
Polo’s writings also helped to spread knowledge of Eastern currencies and banking practices, which facilitated trade between the two regions.
Query Resolution
How long did Marco Polo’s journey last?
Marco Polo’s journey lasted approximately 24 years, from 1271 to 1295.
What was the main purpose of Marco Polo’s journey?
Marco Polo’s journey was primarily a diplomatic mission, as he was sent by his father and uncle, Venetian merchants, to establish trade relations with the Mongol Empire.
What were some of the most significant discoveries made by Marco Polo?
Marco Polo made numerous significant discoveries during his travels, including the existence of the spice trade in the East, the vastness of the Chinese Empire, and the use of paper money.